Chemistry Problem
Mimamsa 2026
Inky Pinky Ponky
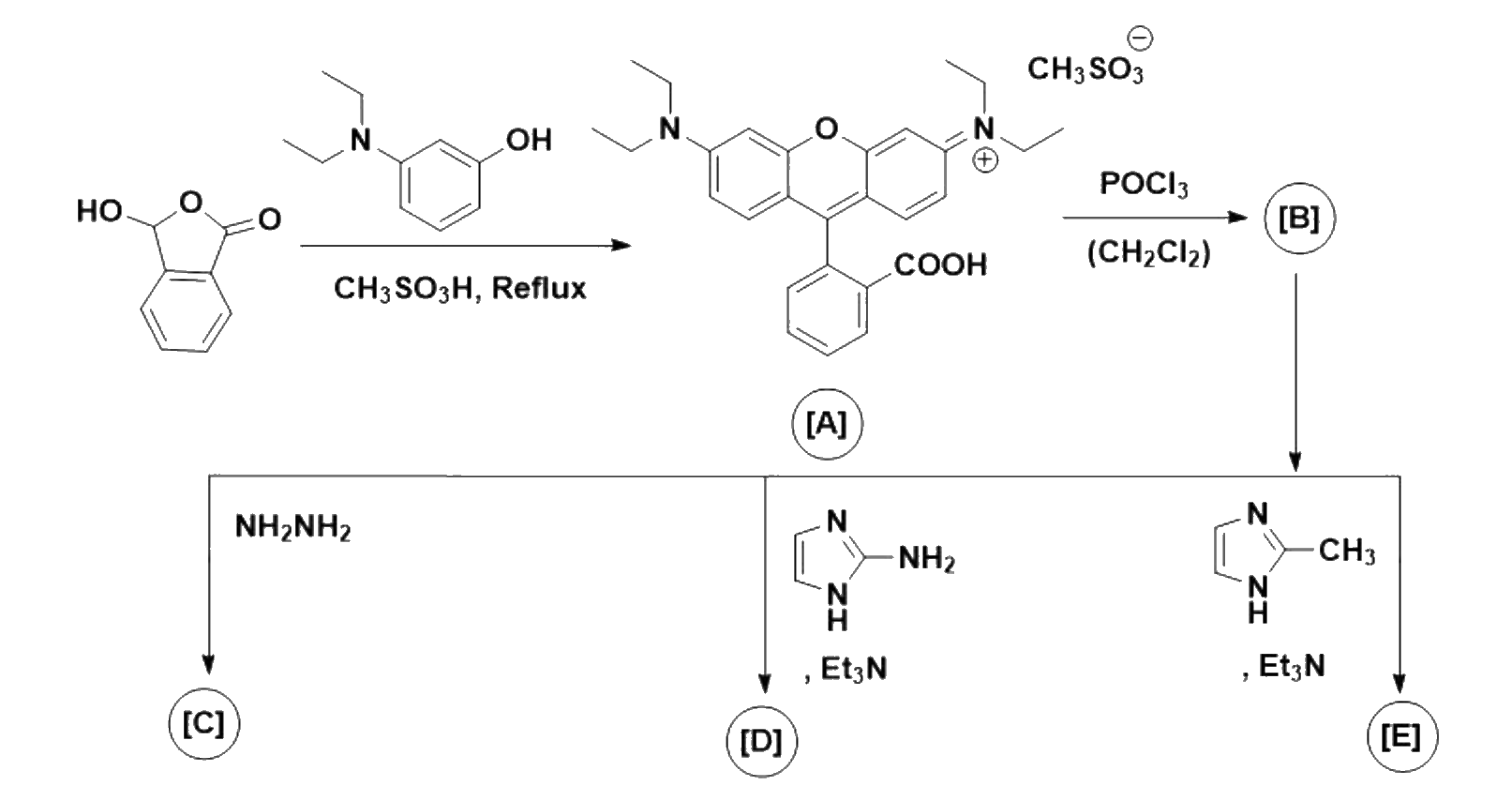
Sonal, an industrial chemist, synthesised the xanthene derivative A as an attempt to create a
new artificial textile dye. On treatment of A with phosphorus oxychloride, the compound B was
obtained, which afforded compounds C, D, and E on treatment with hydrazine, 2-aminoimidazole/triethylamine
and 2-methylimidazole/triethylamine respectively.
1.Give a plausible mechanism for the synthesis of A in the scheme given below.
2. Give the structures of B, C, D, and E.
Sonal observed that A is pink at pH 5.0 and turns colourless when the pH is increased to 8.0.
3.Give a plausible reason for the observed reversible colour change with varying pH.
Next, Sonal experimented with adding 10μM aqueous solutions of Cu2+ and Hg2+ salts to 1mM
acetonitrile/water solution of C, D, and E (maintained at pH 5.0). On adding Cu2+ solution to the
colourless acetonitrile/water solution of C and D, both the solutions turned pink within 1 minute.
But adding Cu2+ to E did not lead to any colour change. However, addition of a Hg2+ salt to the
solution of C and D led to a pink colour appearing only after stirring for 50 hours.
Puzzled by the observations, Sonal measured the absorption spectra of A, C, and D at pH 5.0.
She found that A has an absorption maximum at λmax = 498 nm, while C and D have absorption
maxima at λmax = 320 nm and 345 nm respectively. After 1 minute of adding Cu2+ to C and D,
another peak appeared at λ = 498 nm.
4. Help Sonal explain why the neutral solution of C & D turns pink after the addition of
Cu2+? Also comment on why Hg2+ takes more time for the colour change than Cu2+, when added
to the aqueous solution of C & D.
5. Give a plausible reasoning to explain why the addition of Cu2+ to E does not lead to any
colour change, while D turns pink.